
BNIP3 expression did not differ between low-risk and high-risk MDS patients according to FAB and WHO classifications, and IPSS.
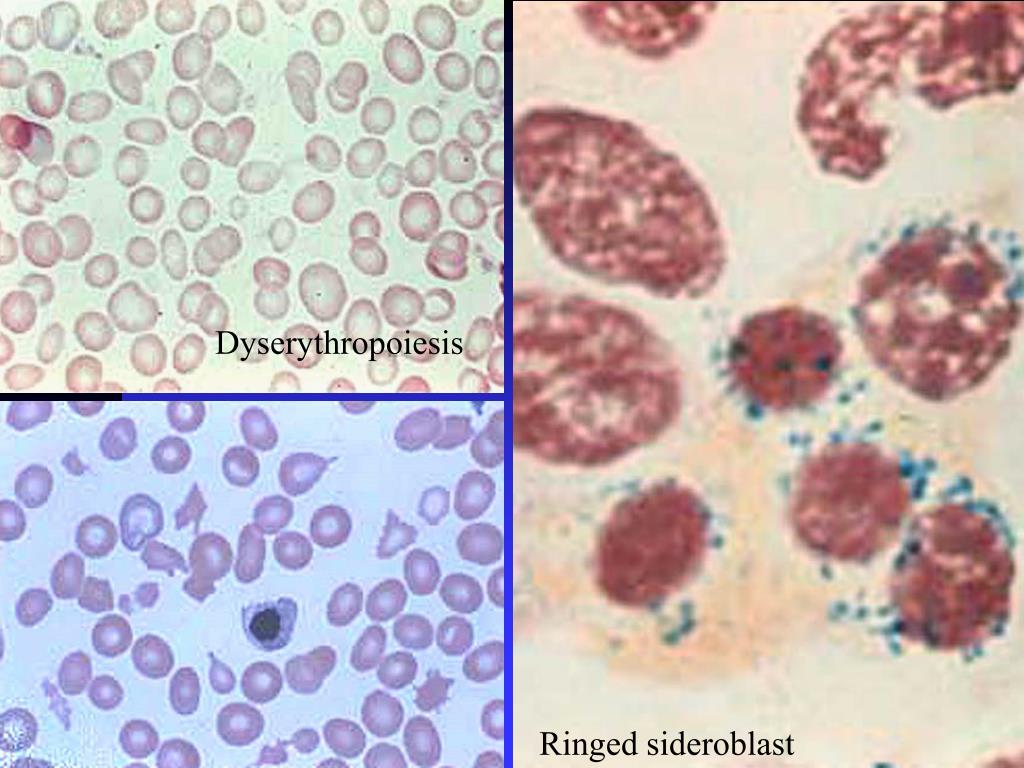
We observed a significant decrease in BNIP3 mRNA expression in total bone marrow cells from AML and MDS compared to healthy donors (AML= 0.52 MDS=0.52 versus healthy donors=1.09 P<0.05). Mann-Whitney and Student's t-test were used for statistical analyses. All assays were performed in lentiviral transduced cells treated or not with 5μM DAC for 72 hours. Apoptosis and autophagy were accessed by flow cytometry. Colony formation was carried out in semisolid methylcellulose medium. ShRNA encoding no specific sequence was used as control. BNIP3 knockdown was performed in U937 cells with specific shRNA-expressing lentiviral vector. Gene expression was evaluated by qPCR and DNA methylation was performed by Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis. The study was approved by the ethics committee and informed written consent was provided. MDS patients were grouped into low-risk and high-risk groups according to FAB (RA/RARS=30 RAEB/RAEBt=25), WHO (RCUD/RCMD/RARS/del5/=29 RAEB1/RAEB2=17) and IPSS (low/INT-1=38 INT2/high=16). Bone marrow aspirates were obtained from 21 healthy donors, 55 patients with MDS and 44 patients with AML at diagnosis. We also investigated the effects of BNIP3 silencing upon decitabine (DAC) treatment in U937 cells regarding colony formation, apoptosis and autophagy. The aim of this study was to characterize BNIP3 mRNA expression levels and DNA methylation status of its 5' CpG island in bone marrow cells from MDS and AML patients, healthy donors and in leukemia hematopoietic cell lines. In primary leukemia cells, BNIP3 expression has been shown to be reduced due to epigenetic modifications however, there is a lack of studies of BNIP3 in MDS. More recently, BNIP3 was identified as a potent inducer of autophagy. BNIP3 is a pro-apoptotic protein, member of the Bcl-2 superfamily, associated with the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancer. It does not store any personal data.In myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), changes in the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins are associated with disease progression and evolution towards acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other.

The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
